Data Management Jobs: Types, Duties, Salaries & More
Learn everything you need to know about starting your career in data management. In this article, Zuar covers the required skills, responsibilities, and roles of data management professionals.

Data managers are important at all medium to large-size business, and staff that are skilled in the data management field are in higher demand then ever.
With the ongoing surge in big data and AI, it's no longer news that businesses now utilize large volumes of data to function and stay ahead in the forever competitive market.
A survey by NewVantage Partners shows that 97.2% of companies are now investing in big data and AI. These companies gather data from a variety of sources to run their businesses optimally and gain more insights on how to best serve and retain their customers.
However, it is not as easy to properly manage these large volumes of data without compromising data integrity, accuracy and adequacy.
These compromises can be prevented and minimized when someone experienced in handling and managing these critical aspects of data is in charge. That's where data managers come in.
What is a Data Manager?
A data manager, sometimes called a data management specialist and other variations, is someone that is responsible for developing and employing effective data management techniques to maintain the integrity and quality of an organization's data.
A data manager oversees the entire process of maintaining data assets, including availability, storage, restoration, organization, quality, integration, transparency, governance, and accessibility of an organization's data by implementing the various techniques available to the data team.
The average salary for a data manager is around $74k [1].

Responsibilities of a Data Manager
In the data management field, a data management specialist is typically responsible for the following duties and responsibilities:
Preserving Data Integrity
A data manager ensures and preserves the integrity of their organization's data. Data integrity refers to the accuracy, completeness, and reliability of data.
They do this by ensuring that the whole process, from data collection to data analysis, is well-supervised and free from any errors or mistakes that could jeopardize the accuracy, adequacy and integrity of an organization's data.
Maintain a Secure Database
A data specialist ensures that the organization's database is secure and safe from theft, loss, cyber-attacks, malware, and unwarranted or unauthorized access.
Ideal Method for Data Collection
It is the data manager's responsibility to sort out the best methods for collecting and transforming data for the organization. An ideal data collection method should be safe, secure, cost-effective, and also guarantee data quality.
One such method involves implementing an ETL/ELT platform (such as Zuar Runner) to ingest data from a variety of sources, model it for analysis, and transport it to the organization's data warehouse.
Data Compliance with Security Regulations
A data manager ensures that all data policies are implemented so that every data collated and analyzed complies with relevant security regulations and laws.
GDPR, PCI, and HIPAA are all examples of data compliance standards that data managers may have to abide by, depending on the type of organization they are employed by and the type of data.
Evaluate Data Sources
Every data source must be evaluated appropriately. This is to ensure that the data is reliable and free from any form of manipulation that could predispose the data to loss of integrity. This data evaluation is monitored and controlled by a data manager.
Disseminating Data
Another key responsibility of a data manager is ensuring that every single employee of their organization has easy access to the data they need; a concept known as data democratization.
By implementing a robust data portal, such as Zuar Portal, data managers can ensure that every stakeholder can confidently access the data they need to make informed decisions, while limiting the access to specific data as needed.

Skills and Requirements of a Data Manager
To perform and deliver exceptional results, a data manager must strike a balance between their technical, managerial and analytical skills. These skills allow them to handle data, as well as data-related tasks, efficiently.
The following are the skills and requirements that are expected of a typical data manager:
- Ability to identify, analyze and interpret various forms of data-related projects, whether of low or high volume.
- Possess time management skills that they can utilize to work on multiple projects simultaneously, and meet deadlines as required.
- Ability to collate, retrieve and organize data whenever the need arises, or the organization requests it.
- Excellent communication skills to interface with both the data management team and other key stakeholders to deliver a productive outcome.
- Have a strong understanding of complex statistical concepts and how to analyze and interpret these concepts.
- Be versed in SQL to handle, deal with and manipulate data in relational databases. Other coding languages can also come in handy, such as Python and data field-specific languages.
- Knowledge and understanding of data protection policies and compliance requirements to be able to implement them as required.
- Experienced and knowledgeable in the aspect of data management as well as its principles, which include data quality, data governance and data security.
- Ability to manage large volumes of data without compromising data quality, adequacy and accuracy.

Typical Day of a Data Manager
A typical day in the life of a data manager varies and also depends on the kind of organization they work for.
However, the tasks and routines to be taken care of are similar in all organizations or companies where the database is appropriately managed.
In no particular order, a typical day in the life of a data manager can look like this:
- Check and respond to data-related emails and messages (and unfortunately many that have nothing to do with the company's data!).
- Create a schedule of priorities for the day, and work towards them to achieve the best results. If your organization has a ticketing system for stakeholders to make requests and flag potential issues, you'll be sure to review what's still outstanding in the queue.
- Update and review data quality and files.
- Correct errors and inconsistencies discovered in the data files.
- Prepare reports and dashboards of project progress for stakeholders.
- Attend meetings with colleagues in the data management team and other departments to discuss things like data-related initiatives, system performance, changes to policies, etc.
- Coordinate with others involved in company data collection, analysis and storage processes.
- Stay ahead of trends, news and best-practices in the data management field, and adjacent fields.

Job Search Strategy of a Data Manager
Searching for a job in data management is similar to any other job search. Before you start applying, you'll want to ensure that your skillset is up to par. This will help ensure that you're not wasting your time applying for positions that you don't qualify for, and the more you learn the more it will differentiate you from others in the job market. You can work on personal projects, take online courses, learn from free online content like YouTube videos, find internships, or even volunteer for data-related projects to help build your resume.
First, it is crucial to identify the job requirements and responsibilities specific to the data manager position. This allows for concentration on jobs that match your skillset. To get clarification on what positions are open and what types of folks the companies want to fill those jobs, go through job postings on sites like Indeed and LinkedIn.
The next step is to structure your data management resume and cover letter around the requirements you're seeing, so you can make sure your resume is optimized to appeal to the hiring company(s).
- Make sure that you highlight your skills and experiences that align with the job's requirements.
- Since many companies employ algorithms to sort through thousands of resumes, incorporating the keywords found in the job description into your resume can boost your chances of an actual human recruiter reviewing your resume.
After these steps, your job search process becomes easier and more promising.

How to Start as a Data Manager
To successfully start your career as a data manager, there are certain steps you should take to smoothly transition into your new role.
1. Learn the Basics
For your new data manager position, it is important to have a clear understanding of everything in the the job description. At a minimum you'll need to learn all the fundamental aspects of data management, which includes data management analysis, types of data and databases, data retrieval, and many others.
2. Acquire Technical Skills
It is one thing to learn about data management; it is another to be able to use and utilize the knowledge practically. It is essential to seek and acquire technical skills to complement your data management knowledge. Some of these skills include learning different programming languages, data analysis tools, and data management systems.
3. Hands-on Experience
After acquiring the required technical skills, the next step will be to garner experience in the field, and in your specific company's business.
4. Pursue Relevant Certifications
Pursuing relevant certifications to show your proficiency in the data management field can help with both your internal job promotion prospects and future job hunting by boosting your resume and raising you above other job applicants.
In our Data Science Career Guide, we list several data certification programs, bootcamps, and training platforms that you can utilize to set you up for success in the job market! Check it out here:


Other Jobs in the Data Management Field
Information Management Specialist
An information management specialist is responsible for managing records, documents, and other IT-related databases for the organization.
The median salary of an information management specialist is around $55k [2].
Data Analyst
A data analyst is not the same as a data manager, although they are often conflated. A data manager focuses on the collection, organization, and protection of data while a data analyst focuses more on the application of that data in decision-making and process improvement.
Under the data analyst umbrella, data quality analysts or data quality specialists help organizations analyze large sets and volumes of data using statistical and data analytical tools to ensure data integrity.
The salary range for a data analyst is $63k-$102k [3].
Business Intelligence Analyst
A business intelligence analyst helps businesses and organizations make strategic and data-driven decisions by providing relevant insights into areas of improvement to promote and boost business operations. Creating easily digestible data visualizations is a key aspect of this role.
The salary of a business intelligence analyst ranges from around $85k-$108k [4].
Data Officer
A data officer (similar to a data steward) oversees the structure and development of an organization's data in compliance with relevant security regulations.
The average salary of a data officer is around $118k [5].
Data Architect
A data architect is in charge of designing the data infrastructure and systems within an organization. They help to present data in an organized manner and also make retrieval more efficient.
The average salary of a data architect is around $155k [6].
Learn more about data architecture here:

Taking the Next Steps
Data management is a rapidly growing career field that offers many benefits. However, without the proper tools and systems in place, data management can be a serious headache.
That's where Zuar comes in. Zuar is the analytics headquarters for organizations of all sizes.
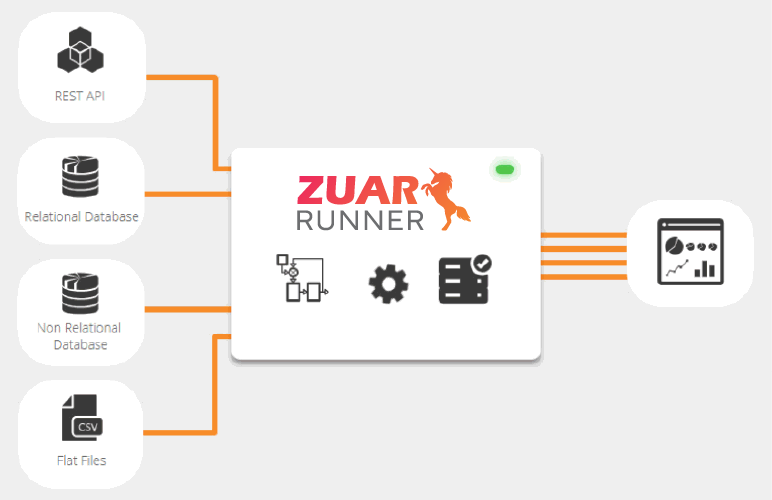
Automate the flow of data from hundreds of potential sources into a single destination for analytics, fully prepped and ready for use, with Zuar Runner.
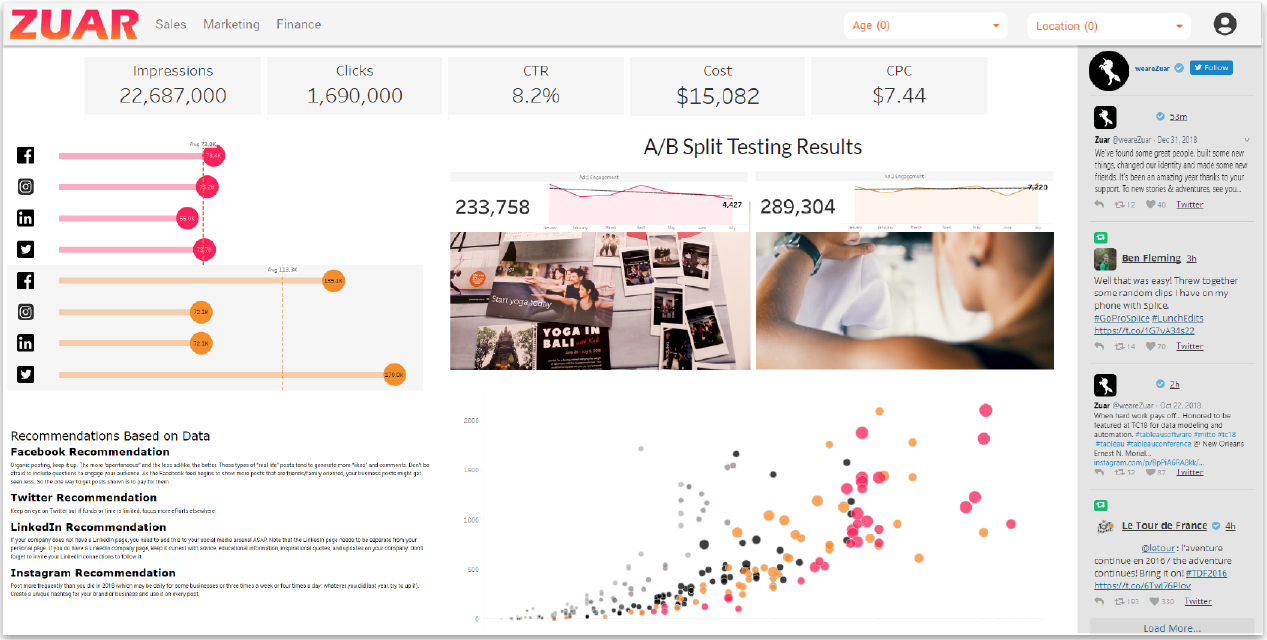
Then with Zuar Portal, you can provide customized, secure, global analytics access to any audience. It's a powerful platform with unrivaled flexibility.
These end-to-end solutions will make life easier for any Data Manager.
Interested in working at Zuar? Click here to see what job openings are currently available.
Interested in our data products or services? Schedule a data strategy assessment with one of our experts:
Article Sources:
- Glassdoor: https://www.glassdoor.com/Salaries/data-manager-salary-SRCH_KO0,12.htm
- Zippia: https://www.zippia.com/information-management-specialist-jobs/salary/
- Glassdoor: https://www.glassdoor.com/Salaries/data-analyst-salary-SRCH_KO0,12.htm
- Salary.com: https://www.salary.com/research/salary/listing/analyst-business-intelligence-salary/minneapolis-mn
- ZipRecruiter: https://www.ziprecruiter.com/Salaries/Data-Officer-Salary
- Glassdoor: https://www.glassdoor.com/Salaries/data-architect-salary-SRCH_KO0,14.htm


