Zuar Runner Integrations: MongoDB
Automate the collection of your data from MongoDB, combine it with data from hundreds of other potential sources, and transport it to the data warehouse of your choosing.
 Schedule a Free Demo
Schedule a Free Demo
Zuar Runner Data Staging Platform
Zuar Runner is an automated end-to-end data pipeline solution that stages data for analytics. Easily integrate data from any data source or API into a database and prepare it for analysis. We set up everything for you as a service, in the cloud or on-premise.
Learn More About Zuar Runner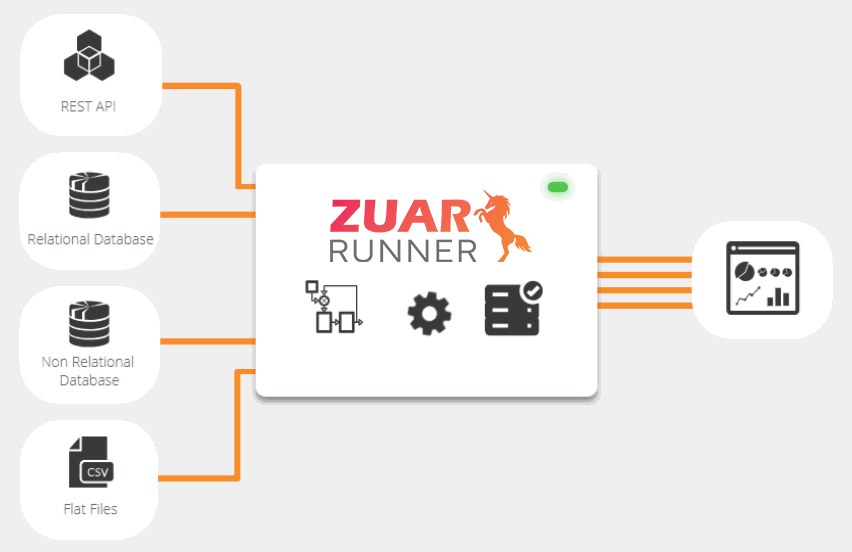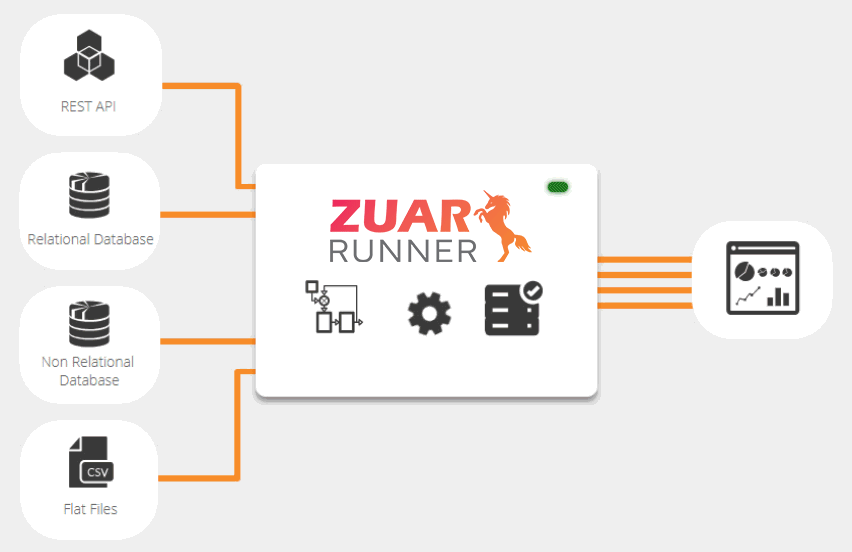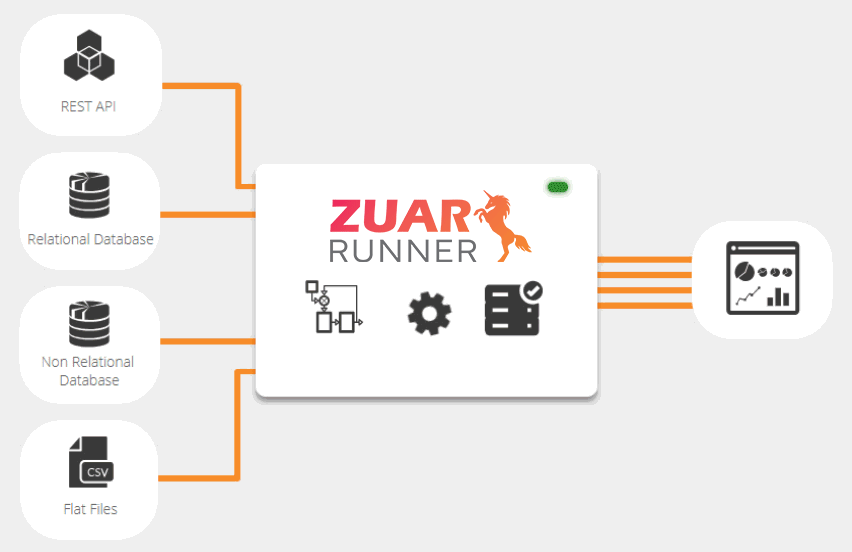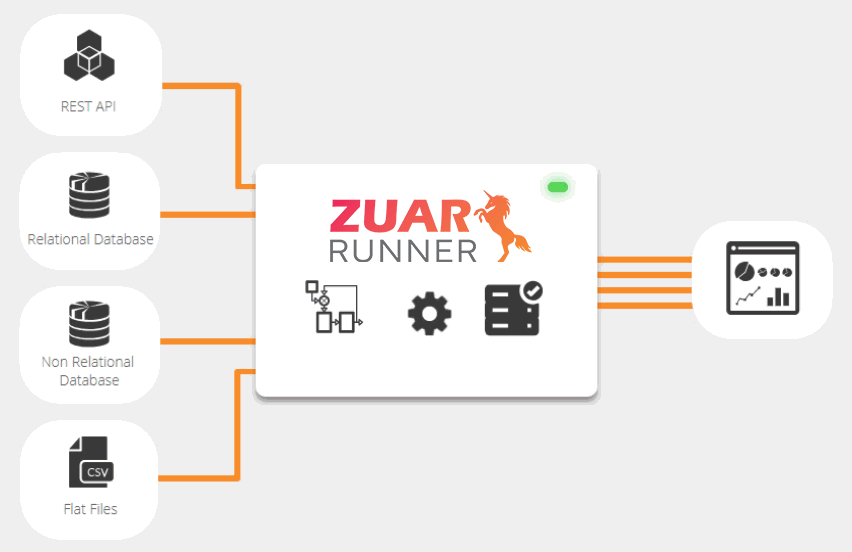
Centralize ALL Your Data
Since MongodDB is a NoSQL database, it is ideal for fast-paced agile environments. But it's not ideal for BI platforms, which prefer tabular, relational database formats.
Perform Complex Analysis
Use Zuar Runner's MongoDB connector to transfer MongoDB data to a staging area where it is modeled for a BI platform, such as Tableau. Our team can also help you create intuitive and interactive dashboards with this data, so your organization can turn raw data into insights.
Learn what other benefits Zuar Runner can bring to your data pipeline by can bring to your data pipeline by scheduling a free consultation today!
"[Zuar Runner] is the best data integration tool that exists"
HANDS ON: How to Set Up Zuar Runner's MongoDB Connector
- 1. Select MongoDB and a destination database.
- 2. Use Zuar Runner to choose specific metrics and dimensions, or transform the data with SQL. Add contextual information to help with analysis. Pivot, aggregate, pre-calculate and create new tables for advanced analytics.
- 3. Schedule each step of the process for automation and monitor the flow of data with built in alerts.
MongoDB Connector FAQs
How do I connect MongoDB to a data pipeline?
To connect MongoDB to a data pipeline, you would typically use an API to extract data from MongoDB and then load the data into your desired data pipeline. The API would allow you to fetch the data in a structured format, such as JSON, that can be easily processed by your data pipeline. For a more automated and flexible solution, you can use a third-party tool, such the ELT platform Zuar Runner, to connect to the API.
Can we connect MongoDB with SQL Server?
Yes, you can connect MongoDB with SQL Server by using a tool such as the MongoDB Connector for BI. This tool allows you to query MongoDB data using SQL, providing a bridge between the two systems. You can also use a variety of other tools and techniques, such as data migration or data integration platforms, such as Zuar’s ELT platform Zuar Runner, to connect MongoDB with SQL Server and move data between the two systems.
Is MongoDB a server or a database?
MongoDB is a database management system. It is a type of NoSQL database that provides a document-based data model, rather than using tables and rows as in traditional relational databases. MongoDB stores data in flexible, JSON-like documents, making it easier to work with complex and hierarchical data. While it can be run as a standalone server, MongoDB is also often used in cloud-based and other distributed architectures.
How do you query data from MongoDB?
Data in MongoDB can be queried using the MongoDB query language, which uses a syntax similar to JSON. Queries can be constructed to select data based on specific criteria, such as matching certain values or conditions. The results of a query can be filtered and transformed, and can be returned in a variety of formats, including documents, arrays, or specific fields within documents.
How does MongoDB store and access data?
MongoDB stores data as documents within collections, with each document being a set of key-value pairs and a unique identifier. It uses a dynamic schema, allowing documents within the same collection to have varying fields and data types. Data can be retrieved using queries based on specific conditions, and results can be transformed and returned in different formats.